What is Analytical Paragraph Writing: Analytical paragraph Is a form of descriptive writing. The writing is analytical in the sense it is based on the input and evidence provided in the question in the form of map, graph, table, cues or chart. There may be a comparison of two or more things or to show choices and preferences also. The data, given in the form of pie charts, line-graphs, bar graphs, maps etc. may be shown as interpreted to show how the things or the trend is different or has become different over the time.
The focus and aim of such a question is to judge the analytical capability and competency of students in creating a writeup in the form of a paragraph sticking to the analytical data or input given in the question.
Click here for Practice Questions on Analytical Paragraph Writing
Syllabus (2022-23): Writing an Analytical Paragraph (100-120 words) on a given Map / Chart / Graph / Cues. One out of two questions is to be answered. (5 marks)
Marking Scheme
Objective: Analysis and Evaluation Marks: 1 × 5 = 5
Marks: 1 × 5 = 5 – Breakup of marks:
- Content (3 marks) i.e. body of the paragraph
- 0.5 mark: Title of the paragraph
- 2 marks: Introduction + Overview
- 0.5 mark: Concluding line
- Expression (2 marks) i.e. usage of words and phrases, spellings, correct grammatical structures etc.
- 1 mark: Structure of the paragraph
- 1 mark: Language use
Types of Analytical Paragraphs
- Data / Graph based
- Excerpt / Cue based
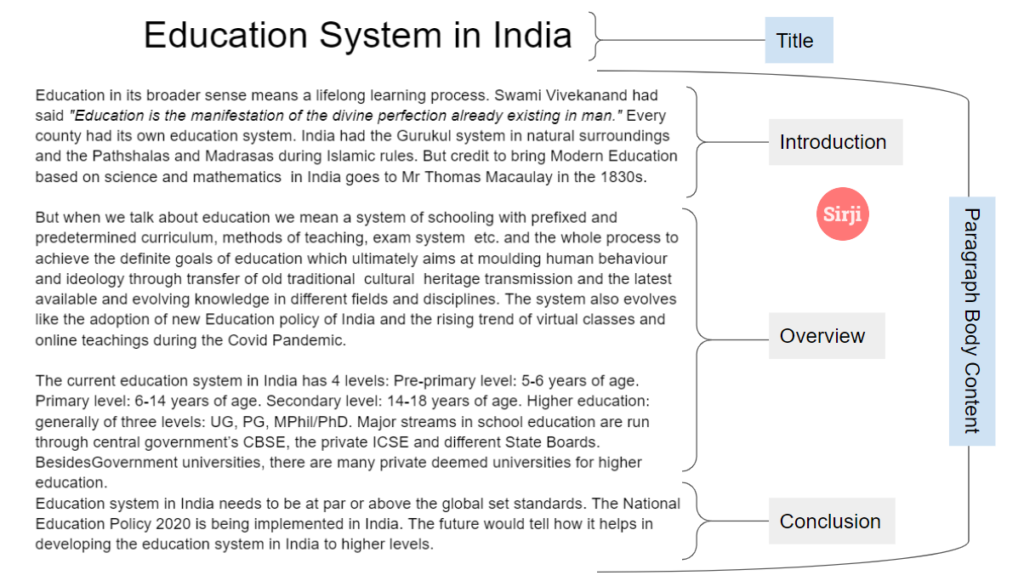
Format of the Paragraph
- Title (Heading) – should be proper and relevant
- Introduction – short and precise to tell how you are going to proceed ahead
- Body (an overview) – preferably single paragraph containing a few arguments (in favour or against)
- Conclusion – it should summarise the arguments incorporated in the body of the paragraph
- Note: The whole matter can be written in a single paragraph and it won’t affect marks.
Note: Inclusion of a single paragraph organisation with a suitable topic sentence supporting sentences and a suitable concluding sentence. No requirement of a title (because the purpose is analysis, not publication). No penalty if title is written.
Example:
Points to Remember
- It is very important for such paragraphs to use the appropriate vocabulary (usage) which is also called ‘functional language’. For e.g., the terms like increase, decrease, plateau, peak and stable, trend etc. should be used accurately in the passage to fetch you marks under expression.
- Don’t use First person Pronouns (I, we, me, us) and not add your own information or data.
- Your analysis should support the given figure or data. Analyse, compare (if needed) data as if you have to prepare a report. Pick relevant points, features to summarise them into an analytical paragraph.
- Avoid repetitions, use superfluous words, spelling mistakes and try to keep it well punctuated.
- Don’t lose relevance! It is very important to stay on topic and not digress (deviate from the main point and subject).
- The word limit is 100-120 words so it is necessary that you are able to convey all the required information briefly.
- Don’t write under the word count and could go a bit over it between 150-180 words.
Click here for Practice Questions on Analytical Paragraph Writing
Marking Scheme (2022-23 Session)
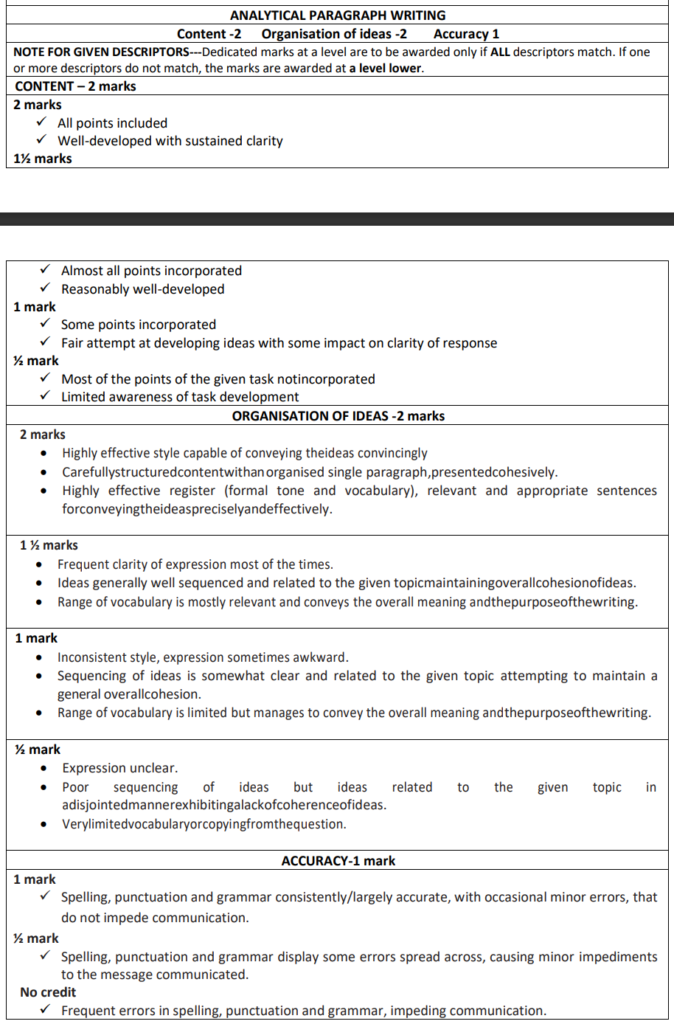
ANALYTICAL PARAGRAPH WRITING
Marking: Content -2 Organisation of ideas -2 Accuracy 1
NOTE FOR GIVEN DESCRIPTORS—Dedicated marks at a level are to be awarded only if ALL descriptors match. If one or more descriptors do not match, the marks are awarded at a level lower.
CONTENT – 2 marks
2 marks
- All points included
- Well-developed with sustained clarity
1½ marks
- Almost all points incorporated
- Reasonably well-developed
1 mark
- Some points incorporated
- Fair attempt at developing ideas with some impact on clarity of response
½ mark
- Most of the points of the given task not incorporated
- Limited awareness of task development
ORGANISATION OF IDEAS -2 marks
2 marks
- Highly effective style capable of conveying the ideas convincingly
- Carefully structured content with an organised single paragraph ,presented cohesively.
- Highly effective register (formal tone and vocabulary), relevant and appropriate sentences for conveying the ideas precisely and effectively.
1 ½ marks
- Frequent clarity of expression most of the time.
- Ideas generally well sequenced and related to the given topic maintaining overall cohesion of ideas.
- Range of vocabulary is mostly relevant and conveys the overall meaning and purpose of the writing.
1 mark
- Inconsistent style, expression sometimes awkward.
- Sequencing of ideas is somewhat clear and related to the given topic attempting to maintain a general overall cohesion.
- Range of vocabulary is limited but manages to convey the overall meaning and purpose of the writing.
½ mark
- Expression unclear.
- Poor sequencing of ideas but ideas related to the given topic in
- a disjointed manner exhibiting a lack of coherence of ideas.
- Very Limited Vocabulary Or Copying From The Question.
ACCURACY-1 mark
1 mark
Spelling, punctuation and grammar consistently/largely accurate, with occasional minor errors, that do not impede communication.
½ mark
Spelling, punctuation and grammar display some errors spread across, causing minor
impediments to the message communicated.
No credit
Frequent errors in spelling, punctuation and grammar, impeding communication.
Official Page
CBSE Answer Scheme: (2021-22 Session)
The question tests the following writing LOs:
▪ convey ideas convincingly using appropriate language
▪ organize the content and structure the ideas logically, sequentially, cohesively
▪ use a range of vocabulary and sentence structure appropriate to the content and context
▪ use of functional language to show comparison, contrast, emphasis, conclusion etc.
Guidance (for awarding marks)
Award 3 marks for content—
1. Topic sentence identifying the two responses to setbacks in the concept map – ½ mark
For Instance:
Setbacks often leave one with a feeling of disappointment and sometimes even worse. / The concept chart given below displays two ways to handle setbacks, for the better or for the worse/ the two ways of processing setbacks – healthy and unhealthy.
2. Any 2 points of contrast/ comparison with evidence – 2 marks
For instance:
Healthy processing helps one learn from and let go the emotions inside. On the contrary, inability to process leads to a block, self-criticism and self-doubt.
Or
An optimistic way of seeing a setback processes the ability to feel, reflect, learn and align. On the other hand, negative perspective of a failure can lead to listlessness, diverted attention, excessive rumination and nonacceptance of failures.
3. Concluding sentence, tied to the content of the topic sentence, showcasing a perspective/ rationalising the importance of healthy processing of setbacks encountered. – ½ mark
For instance, one might want to point to the fact that the responding to setbacks negatively leads to a vicious cycle of undesirable feelings:
It is evident that experiencing a setback leads to feelings of inadequacy and incompetency along with an unwillingness to accept situations. Responding to setbacks the positive way is empowering as it leads to success.
Note—Just listing concept map matter without evidence of analysis carries no credit.
Award 2 marks for organisation & expression—
½ mark—
Inclusion of a single paragraph organisation with a suitable topic sentence supporting sentences and a suitable concluding sentence.
No requirement of a title (because the purpose is analysis, not publication). No penalty if title is written.
½ mark—
use of appropriate functional language to show comparison/contrast & emphasis:
i. Comparison/ Contrast: in contrast with, in comparison to, on the contrary, however, whereas, as opposed to, while, a striking difference, a noticeable difference, despite etc.
ii. Emphasis: in other words, /especially/ specifically/ to emphasise/ to demonstrate/such as/in particular etc.
- full credit 1 mark to be allotted if the functional language has been used consistently
- partial credit ½ mark to be allotted if the functional language has been used occasionally/sparingly
- No credit of marks if functional language is missing (not used at all)
½ mark—
Unity of ideas in the complete paragraph with ideas arranged logically –sentences within paragraph follow expected organizational frameworks*
*[Categorical – in order of importance; Evaluative – a problem is introduced, and the pros and cons are weighed; Comparative – similarities and differences; Cause and Effect; Descriptions-from general to specific attributes]
Accuracy—Deduct from the overall score if the error density is high as this impacts the communicative function.
- ½ mark for a total of 2-3 spelling and grammatical errors
- 1 mark for a total of more than 3 spelling and grammatical errors


